Science and Tech
When will the Netherlands disappear?
Published
3 years agoon
By
Berry Fox
The low-lying nation has been managing water for generations.
Now, total flooding is a threat due to climate change.
Netherlands OVERDIEPSE POLDER — The local phone book in the Dutch region of Noordwaard contains information about a long-gone community: lists of the numbers of houses that have been torn down and left only as square patches of grass in their places.
Noordwaard, formerly a prosperous farming region, is now a vast stretch of reedy marshlands in the southwest of the Netherlands that is purposefully engineered to flood in order to keep surrounding Dutch cities dry. According to a local dairy farmer named Stan Fleerakkers, “the polder used to have big, lovely farms there, acres with potatoes and onions.”
“Now there’s nothing left of it when you drive there.”
The Noordwaard polder was one of 39 such regions that the Dutch government chose for its “Room for the River” program, which involved returning land to rivers. It represents a contemporary reversal of the illustrious low-lying nation’s long-standing tradition of land reclamation.
It also provides a glimpse of the challenges the nation may confront in the future: The Dutch government is working against the time to come up with a solution to prevent one of the richest nations in the world from submerging into the North Sea due to the catastrophic sea level rise predicted as a result of climate change.
Forecasts for sea level rise range from tolerable levels, if the rise is gradual, to catastrophic scenarios that would exceed the capacity of government to respond. Experts are quietly starting to simulate potential futures for the government.
If emissions keep up their current pace, the IPCC projects that sea levels will rise by up to 5.4 meters by 2300 and 84 centimeters by 2100.
In more hopeful circumstances, the celebrated Dutch dikes, storm barriers, pumps, and modifications can handle the situation, but at a cost, and even then, only to a certain extent.
According to Maarten Kleinhans, professor of geosciences and physical geography at Utrecht University, “on the other end of the spectrum is controlled abandonment, which isn’t good since we somehow need to lead 10 million people someplace.” “And there won’t be any investments longer, and local economies will collapse as soon as this becomes known, as soon as the s— hits the fan.”
This is a nightmarish situation, but it’s a serious one, he continued.
If emissions keep on their current pace, the IPCC estimates that sea levels will rise by 84 centimeters by 2100 and as much as 5.4 meters by 2300.

Rising seas
Sea level rise to some extent is already unavoidable due to global warming and ice sheet melting brought on by decades of carbon emissions. Even if nations fulfill their commitments to reduce emissions under the Paris Climate Agreement, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the United Nations body that compiles and evaluates scientific findings, projects a sea level increase of 30 to 60 centimeters by 2100. The probability of an uncontrollable rise decreases when emissions are reduced more quickly. However, the developed world hasn’t yet achieved its goals.
If emissions keep up their current pace, the IPCC projects that sea levels will rise by up to 5.4 meters by 2300 and 84 centimeters by 2100.
The IPCC also cautioned at-risk nations to make preparations since a rise of more than a meter by 2100 is not improbable. Many nations would be helpless to respond in time if the rate of increase continued to rise so quickly and accelerated rises were sure to follow.
A snowball effect caused by rising sea levels enhances the rate at which the problem will persist. In essence, things will only get worse from here: Greenhouse gas bubbles that have been trapped escape, accelerating global warming, and melting snow and ice melts away. The Antarctic ice sheet is also so massive that it pulls the waters toward it gravitationally: Sea water will redistribute away from the South Pole as it contracts, adding to the rise.
According to Michiel van den Broeke, a professor of polar meteorology at Utrecht University, “we’ve lost over half the Arctic ice now, and both the ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica are losing mass and contributing to sea level rise significantly.”
We should take great care not to pass this tipping point because doing so would require us to accept sea level rises of many meters, which the Netherlands is unable to handle. This process is also irreversible at some point.
Depending on the amount of time available for preparation, the Netherlands can tolerate a rise of up to a few meters. The Dutch government claims that present defenses are sufficient through 2050.
The Netherlands was able to cope with merely 40 more millimeters of sea level rise because to flood protection work done over the past 30 years.
Trade-offs are also associated with the options offered. If there is enough time and sand, beaches can be covered in sand. It is possible to elevate the dikes, but doing so puts the people who live there in greater danger if something goes wrong. Additionally, they are permeable; salt cannot be pumped out, but water can. As a result, the land becomes more salinized, which has an impact on Dutch agriculture.
The Dutch take great pleasure in their ability to handle water. The Dutch government is currently making an effort to be proactive.
Storm barriers can be closed, however doing so prevents cargo to the Rotterdam port, which contributes significantly to the Dutch economy. The Dutch fishing sector is also impacted by shoreline interference. Additionally, if the land is below sea level, the rivers that cross it must be pumped through the sea barriers, which uses energy.
There comes a time when preserving the land is not economically feasible.
“A lot is technically feasible. We can build dikes or coastal defenses. However, you must eventually consider whether this is a workable approach, according to van den Broeke. “Retreat is the Plan B. Return a portion of the land to the sea.
The fact that large portions of the nation are already sinking doesn’t help. It is a phenomenon that occurs frequently in deltas around the world: human habitation halts the sedimentation processes that lifted the land initially; ground water extraction further lowers it; and the land contracts under its own weight. The megalopolis of the Randstad, which consists of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, and Utrecht, is the crown jewel of Dutch wealth and industry. It is situated in the west of the Netherlands, which is susceptible and low-lying.
According to Kleinhans, some of the Netherlands’ lowest points are already 10 meters below sea level. “The sea would roughly reach Utrecht, in the center of the Netherlands, if you breached the coast at this time. There is a false sense of security and the situation is truly terrifying.

Creating a future map
The Dutch take great pleasure in their ability to handle water. It has an advantage over other low-lying regions of the world due to its affluence, institutional readiness, and technical know-how.
The regional Water Boards, some of which date back to the 13th century, are autonomous from the national government, which enables them to make plans that go beyond the scope of electoral cycles. Strong relationships between scientists and policymakers have been established, and there is close institutional cooperation.
However, significant flood works have frequently been reactive in response to tragedies like the 1953 storm that burst the dikes and inundated nearly a tenth of the farms in the Netherlands. In addition to destroying homes and drowning tens of thousands of animals, the calamity claimed 1,836 lives.
The Dutch government is currently making an effort to be proactive.
This year, it paid the Sea Level Rise Knowledge Programme, a team of professionals, to keep track on the problem and identify viable solutions. According to Marjolijn Haasnoot, an environmental scientist at the research center Deltares and Utrecht University who has spearheaded the creation of future scenario planning in the Netherlands, the group is focusing on four scenarios.
Two of the scenarios, “Protect Open” and “Protect Closed,” ask for bolstering fortifications using currently available resources with the choice of having storm barriers open or closed. The Netherlands reclaims extra territory from the sea and constructs islands on it in the third scenario, “Advance,” which is an attack scenario.
“Accommodate” is about withdrawal, figuring out which regions of the Netherlands may be kept and which need to be returned to the sea to protect the others. The plan calls for the construction of dikes, water pumping, and the intentional creation of floodplains. Some structures could be made to float; residences could be built on stilts or terps, an ancient type of mound.
Haasnoot has created a model that maps out various future scenarios and decides what measures should be performed in response to each one to aid in choosing the best strategy in preparing for a still unclear future.
Although she predicted that retreat would not be required in the following 100 years, she also cautioned that some of the other possibilities, while technically possible, would cause disruption. For instance, there are costs and trade-offs associated with raising the dikes, reducing the tolerable flood risk, stepping up pumping, and closing the storm barriers.
She also cautioned that what is to come might be more complicated than anything the Dutch have hitherto dealt with. “We need to act quickly since it’s possible that the sea level may rise beyond 2050 at a considerably higher rate, according to Haasnoot. “Some of the behaviors may be quite significant. We have no prior experience with that.”
Roadblocks
The problems associated with sea level rise are difficult for scientists to explain to the public, but they maintain that we must keep trying. They claim that it is politically challenging because it necessitates making present sacrifices in order to achieve a distant and uncertain future.
Even though it won’t happen for a long time, Haasnoot noted that the repercussions are significant and managing the delta will be difficult. “We must take action now and not wait till we see the results.”
The Netherlands is likely to fall short of its goal to cut emissions by 30% from 1990 levels by 2020. Seven political parties, including those on the left and right, came together last summer to enact a climate change law that aims to reduce emissions by 95% by the year 2050.
However, efforts to take more action have been resisted vehemently by individuals who will be impacted.
In October, Dutch farmers blockaded cities all around the country with their tractors in opposition to government initiatives to reduce nitrogen pollution, which is mostly brought on by the farming and construction sectors.
“In Holland, water management costs a lot of money. If we don’t, we’ll be swamped, therefore we have to do it.” – Dairyman Stan Fleerakkers.
Four regional governments stopped the measures as a result of the army being sent in to defend The Hague. Similar protests by construction workers using trucks and diggers were held after that, according to the traffic authority ANWB, causing backups of 380 kilometers.
“The effects of this will be felt for many decades and centuries. It takes a very courageous politician to take on,” remarked van den Broeke of Utrecht University. “It does take strong leadership to accomplish these changes because there is still a sizable portion of the Dutch people that is either unaware of or uninterested in these concerns.”
Professor of physical geography Kleinhans thinks that the general public’s perception of security and faith in flood protection is incorrect.
According to Kleinhans, “It’s a belief founded on the past.” “We’re facing a crisis unlike anything in human history, and possibly in geological history. We have never faced a situation like this, and we are unprepared.

A space for the water
The Netherlands may, however, be left with no choice but to adapt or even withdraw in the end. The Dutch model’s limitations are shown by a group of farmers at the Overdiepse Polder, which is close to the evacuated Noordwaard marshlands.
Stan Fleerakkers and his other 15 farmers were first made aware that their land was under consideration for the Room for the River program—a response to the 1995 Rhine floods, which required the evacuation of 250,000 people—by a brief item in a local newspaper.
Fleerakkers recalled, “We understood if we are going to fight the government, we are going to lose. “We made the decision to work with the government, and this is now our plan. We want to remain here, continue farming, and grow.
Instead of leaving, half of the farmers persuaded the authorities to assist them in staying. The outcome is unquestionably an engineering and planning achievement. The farmers now reside in sizable, Scandinavian-style farmhouses that were recently constructed on terps that were elevated six meters above their meadow grounds and connected to the closest village by roads that were lifted by the same amount. They take their animals up into their high barns for the winter.
The cost of staying is that their land now serves as a basin that will intentionally flood in order to protect the neighbouring cities of Waalwijk and’s-Hertogenbosch. The barrier at the end of their fields, beyond which container ships travel along the Maas, was purposefully lowered to allow river water to enter the fields when it reaches a particular level.
It is anticipated to seriously flood twice a century and once every 25 years.
As sea levels rise further, the question of whether such strategy is scalable arises. The Overdiepse farmers were relocated at a period of luxury, both in terms of time and money. From 1999 to 2015, 16 farmers were relocated. Money was used to grease every step of the procedure.
The historic property of Fleerakkers was generously purchased by the government. While the government constructed the terp and dike works for his new home, he continued to live there and work on it. He is entitled to compensation for any damages and lost crops if a flood ever happens outside of the winter months.
Additionally, if he ever decides to move, the government will purchase his farm at the same price as farms that are not situated in floodplains.
It’s less expensive than when a village floods, according to Fleerakkers. “In Holland, water management costs a lot of money. If we don’t, we will be swamped, and there won’t be any factories or residents left. Everything will be gone.”
Check out on this website which areas are at risk of flooding year after year.
Science and Tech
Cyber attack warning from Microsoft
Published
3 years agoon
25/05/2023By
Berry Fox
Microsoft has warned that Chinese state-backed hackers are targeting critical US cyber infrastructures for intelligence gathering across many industries.
US software giant Microsoft warned that the Chinese cyber actor codenamed “Volt Typhoon” revealed “post-compromat credential access” and “network system discovery-oriented, covert and targeted malicious activities” against critical infrastructure organizations in the USA. .
“Microsoft assesses with moderate confidence that the Volt Typhoon action is aimed at developing capabilities that could disrupt the critical communications infrastructure between the United States and the Asian region during future crises,” the company said in its warning.
While Microsoft informed that the actor in question has been active since mid-2021, it advised customers affected by a possible unauthorized access to close their accessed accounts and change their passwords.
On the other hand, in the news of the American New York Times, citing anonymous sources, it was claimed that the US intelligence was aware of the fact that the aforementioned cyber actor had access to US networks when the Chinese balloon entered US airspace in February.
In the news, it was claimed that Volt Typhoon’s activity in February was focused on the communication infrastructure between the USA and the island of Guam.
The island of Guam is the most critical point in the US strategy to contain China and is home to the largest US military base in the region.
Following Microsoft’s warning, the US has issued a joint Cybersecurity Alert with the cybersecurity authorities of the four countries to draw attention to a set of actions associated with the Chinese state-backed cyber actor.
Joint alert is the United States’ Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and NSA, as well as Australian Signals Agency Australian Cybersecurity Center (ACSC), Canadian Communications Security Authority Cybersecurity Center (CCCS), New The National Cyber Security Center of Zealand (NCSC-NZ) and the UK’s National Center for Cyber Security (NCSC-UK) also participated.
In the warning published, it was reported that the relevant institutions believed that the actor identified by Microsoft could apply the same techniques to other countries and other sectors.
Stating that one of Volt Typhoon’s main tactics is to hide using built-in network management tools, the institutions included the information, “Some of the built-in tools used by this actor are wmic, ntdsutil, netsh and PowerShell.”
Science and Tech
Creator of ChatGPT: My biggest fear is the possibility of harming the world
Published
3 years agoon
17/05/2023By
Berry Fox
“My biggest fear is that we, as the tech industry, may cause significant damage to the world,” said Samuel Harris Altman, Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of OpenAi, which developed ChatGPT.
Speaking at the US Senate Judiciary subcommittee, OpenAi’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Samuel Harris Altman, said: “My biggest fear is that we, as the technology industry, may cause significant damage to the world. I think it could be different,” he said.
“As with all technological revolutions, I expect a significant impact on employment, but it’s very difficult to predict exactly what that impact looks like,” said Altman, warning the Senate that ChatGPT technology “could go to a very bad place”.
According to the newspaper Oxygen, Samuel Harris Altman, speaking about the growing popularity of ChatGPT and the positive and negative possibilities of artificial intelligence, acknowledged that the government should step in to ensure these changes are managed.
In the 3-hour meeting, Altman advised the US Senators to establish an independent mechanism to conduct licensing audits of artificial intelligence technologies, and stated that this would allow a set of security standards, including the assessment of their dangerous capabilities, to be established.
This way, Altman said, we can ensure that the models “can’t self-replicate and move on their own.”
Speaking to the committee meeting, some senators also warned about corporate cooperation in the artificial intelligence market, pointing to the problems that will be faced if a small number of technology companies dominate this sector.
Science and Tech
Warnings about artificial intelligence from Geoffrey Hinton, scientist who left Google
Published
3 years agoon
02/05/2023By
Berry Fox
Scientist Geoffrey Hinton, one of the pioneers in the field of artificial intelligence, made statements that warned against progress in this field.
Hinton, 75, recently resigned from his position at Google.
“Now I can talk about what the dangers are,” Hinton said in an interview with the BBC, adding that some of these dangers are “very frightening.”
The scientist, who has British and Canadian citizenship, says that chatbots, known as chatbots, may soon exceed the information capacity of the human brain.
Hinton played a role in reaching the present point of artificial intelligence with his research on deep learning and artificial neural networks.
Advanced systems like ChatGPT are at the center of warnings about the future as well as the possibilities they provide.
Hinton also draws attention to this point:
“Right now, GPT-4 can far outshine a human in the amount of general knowledge it holds. In terms of reasoning, they are not equally good, but they can make simple reasoning.
Considering the rate of progress, we know that these systems will become more effective very quickly. And that should worry us. At the moment, as far as I know, they are not smarter than us. But they may soon be smarter.”
In the article he wrote for the New York Times, Hinton emphasizes that “bad people” can do “bad things” with artificial intelligence.
Answering the BBC’s question about this point, Hinton replies, “This is one of those nightmare scenarios”:
“Suppose one of the villains, Putin, allows robots to create their own sub-purposes. This may eventually lead to sub-objectives such as ‘I need to get more power’.
Hinton continues:
“I came to the conclusion that the type of intelligence we create is very different from what we have.
“We are a biological system, but these are digital systems. The biggest difference with digital systems is that you can make multiple copies of the same size.
“All these copies can learn different things but instantly share their knowledge with each other. So it’s like you have 10 thousand people and one of them learns something and the others have this information at the same time. That’s why these chatbots have more information than any human.
Regarding his departure from Google, Geoffrey Hinton said, “I wanted to say good things about them. “If I had said these things while I was working there, they wouldn’t have been effective enough,” he said.
Science and Tech
New planet twice the size of Earth discovered
Published
3 years agoon
01/05/2023By
Berry Fox
Scientists announced the discovery of a new planet called TOI-733b, which is stated to be about twice the size of Earth.
Scientists have discovered a new planet about twice the size of Earth and covered with oceans.
It is stated that this planet, called TOI-733b, is only one of more than 5 thousand exoplanets that have been known after the first discovery in the 1990s.
TOI-733b was found 245 light-years away by NASA’s telescope TESS. It has been noted that the relative similarities of the planet orbiting a star slightly smaller than the sun in a period of only 4.9 days could play a key role in understanding the formation of planets in the universe.
THE INTERESTING SIDE OF THE PLANET ‘SIZE’
It was stated that the particularly interesting aspect of TOI-733b for researchers is its size.
Density measurements on the planet from a distance show that it has either lost the atmosphere it once had or is a planet that is completely covered with water.
However, several data points indicate that TOI-733b’s atmosphere is slowly depleting, which may be due to its proximity to its star’s heat.
Other theories suggest that TOI-733b lost its hydrogen and helium and instead retained an atmosphere filled with water vapor or regenerated a secondary atmosphere made up of heavier elements.
“ONE KEY PIECE”
The research on the planet by Astronomy & Astrophysics noted how exciting and “interesting” the discovery of the planet is in the field of astronomy, saying it has the potential to be “a small but key piece to solving the big puzzles in exoplanet science”.
“With the promise of increasingly in-depth theoretical analysis and high-precision follow-up by current and future facilities, we appear to be on our way to answering important questions about planet formation and evolution,” the research said.
Science and Tech
Research: Eating french fries can cause depression
Published
3 years agoon
28/04/2023By
Berry Fox
New research; found that fried foods are not only beneficial for physical health, but also cause mental disorders such as depression.
According to a study published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, data from more than 140,000 people who consumed fried food for 11 years revealed a link between fried food consumption and anxiety disorder and depression.
The data obtained from the UK Biobank, which contains the health data of 500 thousand people in the United Kingdom, was analyzed by a group of scientists in Hangzhou, China.
Studies have shown that eating french fries increases the risk of anxiety disorder by 12 percent and the risk of depression by 7 percent.
The researchers put forward the thesis that the results obtained may be related to a chemical called acrylamide that occurs during the frying process.
However, the researchers stressed that the results from the study are preliminary, and there is no need to give advice to stop eating french fries.
“There is no need to panic about the ill effects of fried food,” Yu Zhang, co-author of the article, told CNN.
Science and Tech
Microsoft to pay US fine for sanctions violations
Published
3 years agoon
07/04/2023By
Berry Fox
It was reported that the US technology company Microsoft will settle in the investigation carried out on the grounds that it violated the US export controls and sanctions, and will pay a total fine of $ 3.3 million.
In a statement made by the US Department of Commerce, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) of the Department of Commerce and the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) of the US Department of the Treasury gave a total of $ 3.3 million to Microsoft for violations of US export controls and sanctions laws. sentence was reported.
In the statement, which stated that Microsoft voluntarily disclosed the alleged violations to both BIS and OFAC, it was noted that the company cooperated in the joint investigation carried out by BIS’s Export Enforcement Office and OFAC.
In the statement, Microsoft reportedly took corrective measures after discovering the ongoing situation that preceded export controls and sanctions in connection with Russia’s war in Ukraine.
In the statement, it was stated that BIS imposed an administrative fine of 624 thousand 13 dollars on Microsoft, while OFAC imposed a fine of 2 million 980 thousand 266 dollars for 1,339 violations of the sanctions regulations covering Ukraine/Russia, Cuba, Iran and Syria.
In the statement, it was stated that Microsoft was given a loan of $ 276 thousand 382 by the BIS, subject to meeting its requirements under the settlement agreement with OFAC, and the total penalty amount was $ 3 million 327 thousand 897.
The U.S. Treasury Department said in a statement that most breaches between 2012 and 2019 were related to sanctioned Russian entities or individuals in the Crimea region, as a result of Microsoft’s failure to identify and block the use of its products by sanctioned parties.
Science and Tech
Feature that will delight Microsoft Teams users
Published
3 years agoon
05/04/2023By
Berry Fox
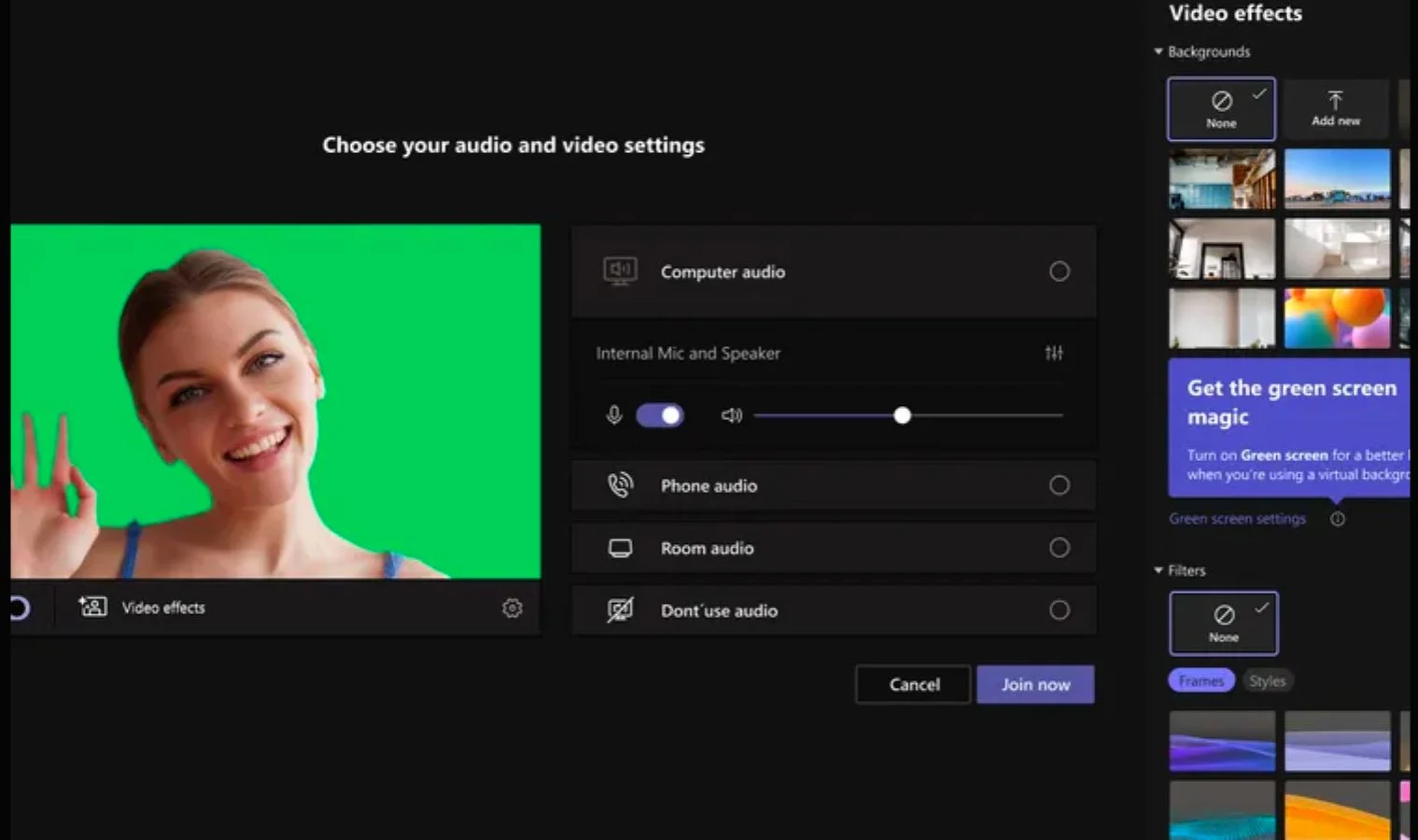
A new feature has been introduced for Microsoft Teams. Thanks to this feature, the background of your conversations will now look more realistic.
Microsoft is adding a new green screen feature for Teams. This new feature, which will make the background appear more realistic in video calls, will also increase the virtual background experience.
NEW FEATURE WILL SEPARATE THE USER PROPERLY FROM THE FUND
The new feature was announced in a blog post. There are some nuances to use this feature in Microsoft Teams. The wall or wallpaper in the background should be unstained and should be preferred plain without anything like a poster or frame on it. Users need to apply the background effect to enable the green screen effect and choose the background color carefully for the effect to be of better quality.

On the other hand, the effect works much better if you already have a green screen. But of course this is not a requirement.
The feature can be used on Windows devices and versions with Intel processors on macOS. So if you’re using a Mac with an M1 or M2 processor, you can’t use this feature right now.
The green screen feature, which does not currently support the together mode, is open to everyone. To enable it, you need to apply a background effect in your Teams meeting. You can choose the color of the wall behind you or green if you have a custom green screen.
Science and Tech
Russian satellites will offer internet access in the Arctic in 2026
Published
3 years agoon
05/04/2023By
Berry Fox
Thanks to the Russian spacecraft Skif, people in the Arctic will have access to the internet in 2026, the TASS news agency reported on Friday.
In the statement made by the press service of the Sphere Congress, it was noted that internet access will be provided in the North Pole from 2026 with the Skif satellites belonging to the project.
According to the press service, there is almost no Internet access in the Arctic. People in the region can access the Internet using American satellite phones, but this method is slow and expensive to access the global network.
In October 2022, Russia successfully placed a Skif-D satellite into orbit using the Soyuz-2.1b launch vehicle. In the future, eight Skif satellites are planned to enter orbit to form a multi-satellite orbital constellation.
Science and Tech
Apple stopped production of the M2 processor for a while
Published
3 years agoon
05/04/2023By
Berry Fox
According to new reports, Apple has stopped the production of M2 processors for a while.
Although Apple seems to be progressing well according to the numbers, it is having problems in some parts. Apple, which stopped the production of the iPhone mini series on the grounds that it did not see ‘as much demand’ as it wanted, this time prefers a similar scenario for the M2 processor.
APPLE’S SALES ARE DROPPING TOO
In the news, behind this decision of Apple lies the expectation of a decrease in Mac sales. In the news reported by SamMobile, it was also written that Apple’s decision will affect Samsung. According to reports, Apple completely stopped the production of M2 processors for MacBooks in January and February.
According to the allegations, although production started partially in March, it is produced in a much more limited way compared to the same period last year.
The source of these claims, which started in the South Korean media, is the decline in global demand for computers.
Apple, which has a significant share in computer sales, is also affected by this decline. Actually, it’s not a surprise for Apple either. There was a statement from Apple that ‘the PC market is in a difficult situation’ and that they ‘may have difficulties in the short term’.

Another crazy move came from Elon Musk, who bought Twitter.
Elon Musk replaced Twitter’s logo with Dogecoin.
Elon Musk has made a change that will be on the agenda on the social media platform Twitter. Musk replaced Twitter’s logo with Dogecoin.
After the logo started to be displayed on the Twitter homepage, there was a great increase in Dogecoin, gaining more than 30 percent in value. There was no official statement.
While there was no official statement from the company after the change, Elon Musk aroused curiosity with his tweet.
In the cartoon in the tweet, the Shiba dog gives his license to the police he was caught while driving. The blue bird photo on the driver’s license says, “That’s the old photo.”
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) April 3, 2023
Advertisement

Top 5 Wedding Photographers in the Netherlands (2026 Guide)

5 intimate wedding venues in the Netherlands

New Year’s Eve in Amsterdam 2025-2026: Best Parties, Fireworks, and Traditions

Amsterdam Christmas Markets 2025: Dates, Locations, and The Ultimate Holiday Guide

NL-Alert: The Netherlands’ Essential Emergency Alert System

Best Outdoor Activities in Amsterdam | Natural and Cultural Wonders

Major disruption in train services between Rotterdam and Den Haag until December

More than 800 film producers and actors in the Netherlands call for sanctions against Israel

Scientists warn: Ultra-processed food is as addictive as cigarettes

The price of a pack of cigarettes in Belgium will be 10 euros

There will also be an increase in the consumption tax on soft drinks in the Netherlands

Wanted murder suspect Bretty Dorder in the Netherlands was caught!

Fighting dog feces: Tracing feces with DNA

Ajax – Feyenoord: 0-4 (MATCH RESULT)

Armed attack in Rotterdam, Netherlands: 3 dead

Home Ownership Rate Declines in European Union Countries

Van Gogh’s stolen painting was found after 3.5 years

Pakistani cricketer who put a bounty on Geert Wilders’ head gets 12 years in prison

Fossil fuel protest in the Netherlands on the second day: 500 activists detained

Ajax-Feyenoord derby canceled due to incidents

Bicycles in Amsterdam: The Art of Commuting

Amsterdam’s Cycling Culture: A Lifestyle to Embrace

Amsterdam’s Bike-Friendly Neighborhoods

The Wheel Revolution: How Amsterdam’s Bicycles Reshaped the Cityscape

How to eat cheap food in Amsterdam?

Arts and Entertainment: Amsterdam Guide 2023

Heartbeat of Amsterdam: Exploring the Iconic Bicycles

How to Rent a Bike in Amsterdam

Billboards of OnlyFans model spark controversy in UK

Dutch Supreme Court: Israeli soldiers cannot be tried in our country

Amsterdam fine for loud car engines and exhausts

Verstappen equals F1 record

Exploring Amsterdam’s Best Laptop-Friendly Cafés for Digital Nomads

How Netherlands Emergency system works?

2 Russian warplanes approaching Dutch airspace intercepted

In another city in the Netherlands, a bacteria warning was issued in drinking water

Warning from TK Maxx in the Netherlands: Electric leakage in the adapters!

Rising rents in the Netherlands led citizens to Belgium

Children’s bicycle helmets are recalled for safety reasons in the Netherlands


