2022 witnessed many groundbreaking new developments in science that gave us hope for the future, as well as enabling us to see more clearly some of the dangers that await our planet and humanity.
The experimental results of the drug developed by Eisai and Boigen companies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s revealed that the drug slowed the progression of the disease when administered after early diagnosis.
Although the detailed results of the experiment have not been published yet; even the limited data shared was enough to create hope in the scientific world.
Lecanemab removes toxic beta-amyloid proteins that accumulate in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Scientists said it was a “historic development”
James Webb, the most powerful telescope of the American National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), shared for the first time clear images of the universe that we have never seen before.
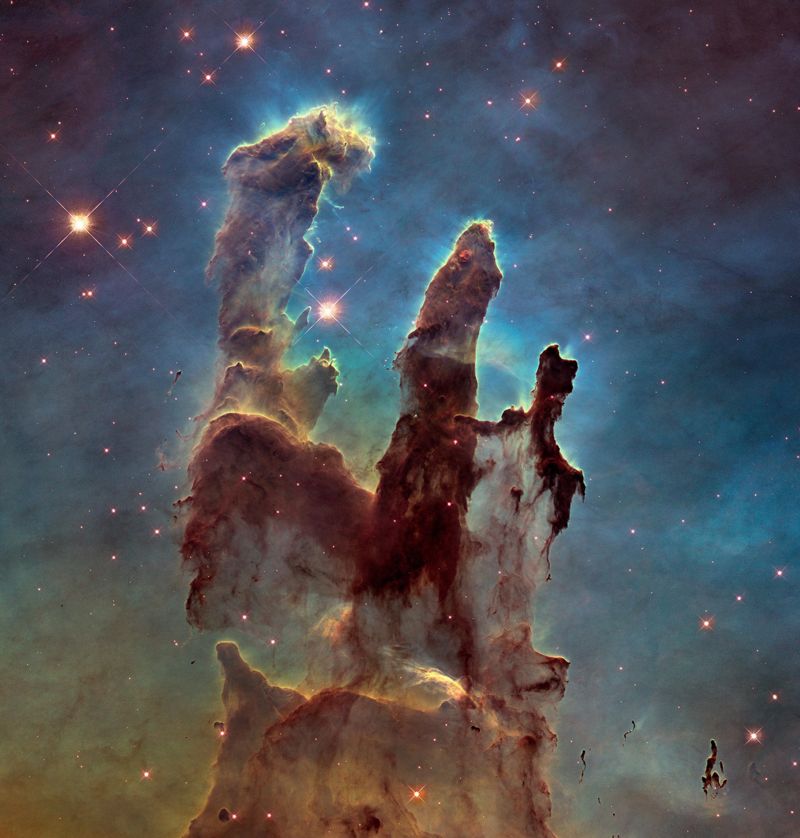

The James Webb Telescope was sent into space in December 2021 and reached the point where it will observe in space on January 25, 2022.
The telescope has so far discovered millions of galaxies, captured incredible images of Jupiter and Neptune, and shared the deepest, most detailed picture of the universe ever taken.
The Dart mission, which NASA aimed to change its orbit by hitting an asteroid, was successfully completed.
The mission aimed to detect the difficulties of preventing a large-scale asteroid from hitting Earth.
Launched in November 2021, the spacecraft hit the asteroid Dimorphos, 11 million kilometers from Earth, with a direct hit.
Nuclear fusion energy has “historic success” in the USA; For the first time in a fusion experiment, more energy than needed for the process could be produced.
Nuclear fusion is thought to hold the potential for an unlimited source of clean energy.
The experiment was conducted at the National Ignition Facility located at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in California.
This process occurs when two lighter atomic nuclei are forced to combine and form a heavier nucleus.
A 13-year-old girl in England with leukemia has completely defeated cancer with the help of a revolutionary treatment called “nucleobase editing”
Nucleobase editing is a bioengineering method that allows tampering with DNA bases and was discovered just six years ago.
Nucleobase editing allows scientists to focus on a specific part of the genetic code and change the molecular structure of one base to convert it to another, thereby encoding new genetic instructions.
A large team of doctors and scientists used this method to design a new type of T cell that can capture and kill Alyssa’s cancerous T cells.
In England, scientists managed to change the blood group of the kidneys to be used for organ transplants.
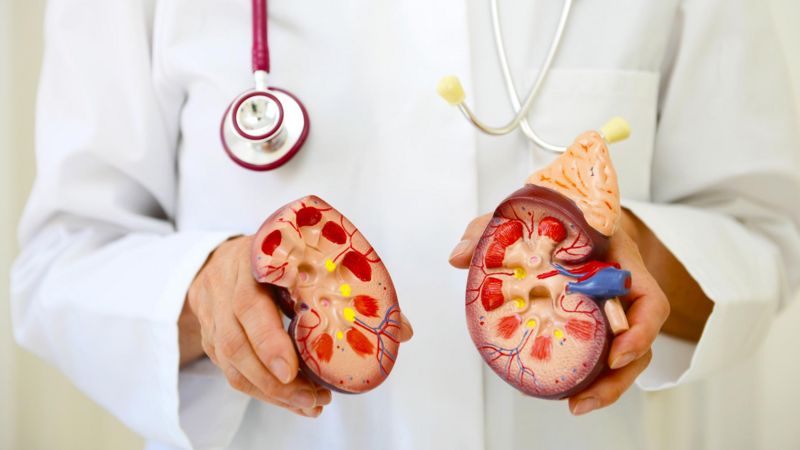
It is stated that this could be an invention that could increase the supply of organs for transplantation and would have special implications for groups that often struggle to find suitable donors.
There is no kidney transplant from people with different blood groups, but it is possible to transfer the kidney to any patient by converting the blood group of the kidney to type 0 (zero).
Researchers in England rejuvenated the skin cells of a 53-year-old woman to the equivalent of those of a 23-year-old woman.
Scientists in the city of Cambridge believe they can do the same with other tissues in the body.
Research; It aims to develop treatments for age-related diseases such as diabetes, heart disease and neurological disorders.
The skin cell rejuvenation technology builds on the techniques used to create the cloned sheep Dolly over 25 years ago.
Dutch scientists have detected for the first time that small plastic particles (microplastics) are found in human blood.
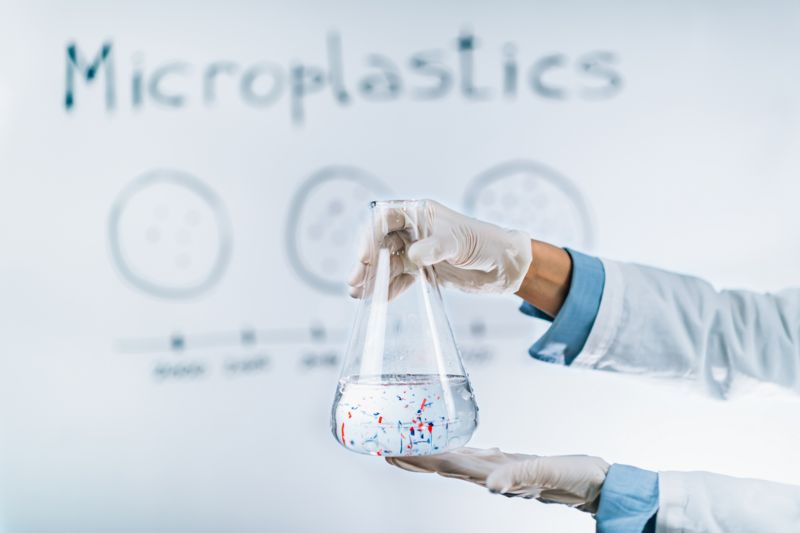

As a result of the tests performed by the experts of the Free University of Amsterdam (Vrije Universiteit), microplastics were detected in the blood of 17 of the 22 people who participated in the study.
It is still not known exactly how harmful the plastic particles are, but one of the researchers, Prof. Dr. Marja Lamoree says the existence of microplastics is itself a cause for concern.
The world’s largest known plant has been discovered off the coast of Australia.
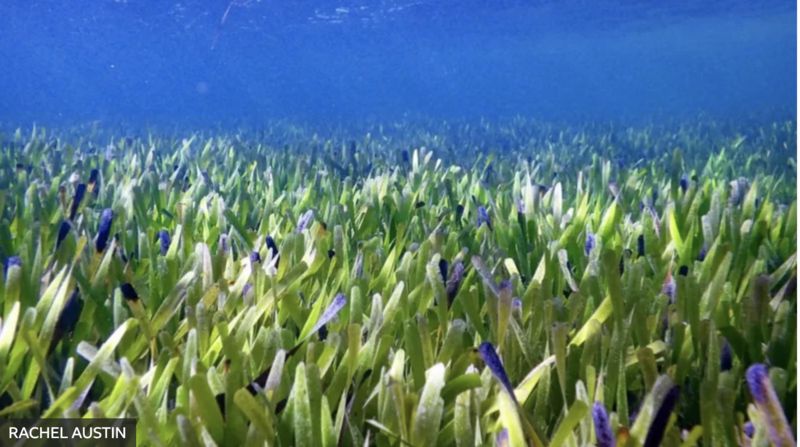

Researchers estimate the age of the seagrass, the size of 20,000 football fields, to be about 4,500 years old.
Geneticists point out that this great underwater meadow in Western Australia, which they have studied for different purposes, is actually a single plant.
The plant is believed to have spread from a single seed at least 4,500 years ago.
Researchers from the University of Western Australia say the seagrass covers an area of about 200 square kilometers.
The team accidentally discovered the plant in Shark Bay bay, about 800 km north of Perth, on the westernmost tip of Australia.

